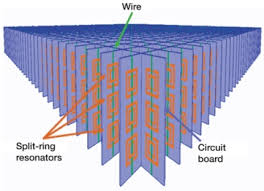
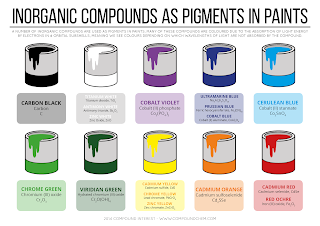
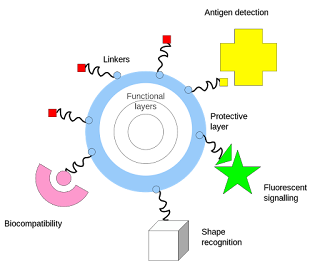
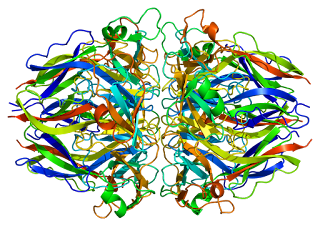
Submit your abstract under the session Inorganic material for Material Science Congress.
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks C-H bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound, but the distinction is not defined or even of particular interest.
Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation.
Some simple compounds that contain carbon are often considered inorganic. Examples include carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, carbides, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms, which means that describing a chemical as inorganic does not obligately mean that it does not occur within living things.
For more: http://www.globalepisteme.org/Conference/material-science-conferenceTo register: http://globalepisteme.org/Conference/material-science-conference/registrationSubmit your abstract: http://globalepisteme.org/Conference/material-science-conference/submitabstract
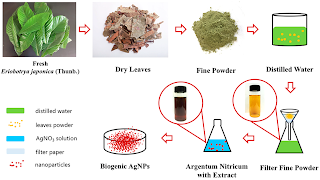
Submit your abstract under the session Biotic materials for Material Science Congress.
Biotic material or biological derived material is any material that originates from living organisms. Most such materials contain carbon and are capable of decay.
The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago. Earlier physical evidences of life include graphite, a biogenic substance, in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in southwestern Greenland, as well as, "remains of biotic life" found in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia.[5][6] Earth's biodiversity has expanded continually except when interrupted by mass extinctions.Although scholars estimate that over 99 percent of all species of life (over five billion)[8] that ever lived on Earth are extinct,[9][10] there are still an estimated 10–14 million extant species,of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86% have not yet been described.
For more: http://www.globalepisteme.org/Conference/material-science-conferenceTo register: http://globalepisteme.org/Conference/material-science-conference/registrationSubmit your abstract: http://globalepisteme.org/Conference/material-science-conference/submitabstract